
Blockchain
A blockchain is a distributed database which is used to maintain a continuously growing list of records, called blocks. Each block consists of two sections; one is timestamp which contain the update time information and another contains a link to the previous block. A blockchain is a managed by a peer-to-peer network collectively adhering to a protocol for validating new blocks. Once a block is recorded the data in the given block cannot be altered without the altering all subsequent blocks and collusion of network. On functional point of view, a blockchain can serve as “an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and effectively and in a verifiable and permanent way. The distributed ledger itself can also be programmed to trigger transactions automatically.”
History
The first blockchain was conceptualized by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 & implemented as a component of the digital currency which is known as bitcoin. For bitcoin the blockchain act as a public ledger for all the transactions. Through the use of peer-to-peer network and a distributed timestamp server a blockchain database is managed autonomously. Bitcoin is a use case of blockchain. Blockchain made the bitcoin the first digital currency which solves the problem of double spending without requiring a trusted administrator.
Opportunities
Weaknesses
Threats
FinTech
FinTech is a short term for financial technology is an industry composed of companies that uses new technology and innovation. FinTech companies belong to the banking and financial service sector and they compete with traditional financial institutions and intermediaries in the delivery of financial services. A fintech company can be both startup and established financial and technology companies trying to replace or enhance the usage of financial services of incumbent companies. Today the fintech industry is growing at a rate of 23% year on year.
Why FinTech
The year 2007-08 during Global Financial Crisis when all the financial companies were melting down. At this time the FinTech companies started to grow from a corner of the financial world. The reason for the raise of the fintech companies are as follows:
Blockchain in FinTech
The raise of fintech companies take place when the banking and financial companies stop the innovation in financial sector. The biggest challenge a fintech company is trust. How to make people trust them, and how to make a safe and secure financial product. Banks and financial companies have huge cash reserve using which they create best in class secure network on which banking transactions take place. Fintech companies lacks fund which restrict them in developing or procuring high security system.
Here comes the blockchain technology. Blockchain is cheap in terms of developing and also highly secure. With blockchain a fintech company will be able to manage their financial product very easily and securely. With blockchain technology fintech companies are now able to create various financial products with very less amount of budget to serve their customer. As blockchain is a series of block the company can track the complete life cycle of a financial transaction. Blockchain has given the opportunity to create secure and safe financial product and providing fintech the opportunity to bring innovation in the financial sector.
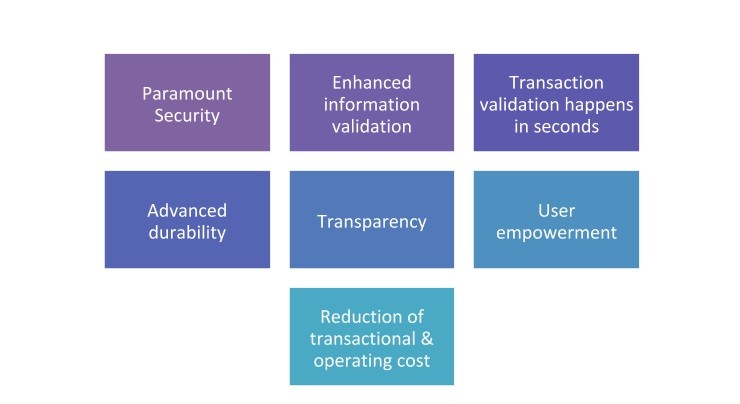
Before we look into the Blockchain applications in the financial industry, let us the see the Blockchain’s benefits:
Overstock
Overstock is one of the largest US online retailers, decided to focus on building the crypto-capitalism future. In the year 2016 Overstock launched their blockchain based trading platform for public and private. This platform will allow instant and secure share trading online.
Openbazar
Openbazar is a startup which introduce fee-free online marketplace similar to eBay which is been powered by Blockchain. The platform promotes an active exchange of goods and services between two parties without relying on a risky centralized authority. It enables more and more people to start their e-commerce business without paying for any additional e-commerce tools.
Sentbe
Sentbe is a fintech company. They provide P2P micro-payments. While many companies provide similar kind of service, Sentbe’s service completely depends on the blockchain. Sentbe offers 60% less expensive service for sending money aboard and offers cash pickup.
Abra
Abra is also a P2P micro-payment service provider whose main target market is US. Abra provide free P2P money transfers and receiving pay-outs in bank or in cash.
There are many more blockchain use cases given below:
Digital Content/Documents, Storage & Delivery
Startups: BitProof, Blockcai, Ascribe, Artplus, Chainy.Link, Stampery, Blocktech (Alexandria), Bisantyum, Blockparti, The Rudimental, BlockCDN
Authentication & Authorization
Startups: The Real McCoy, Degree of Trust, Everpass, BlockVerify
Digital Identify
Startups: Sho Card, Uniquid, Onename, Trustatom
Marketplace
Startup: MyPower
Smart Contracts
Startups: Otonomius, Mirror, Symbiont, New system Technologies
Real Estate
Startup: Factom
Diamond
Startup: Everledger
Gold & Silver
Startups: BitShares, Real Asset Co., DigitalTangible (Serica), Bit Reserve
Review/Endorsement
Startups: TRST.im, Asimov (recruitment services), The World Table
Internet of Things
Startup: Filament (industry IOT), Chimerainc.in, ePlug
Network Strucutre and APIs
Startups: Ethereum, Eris, Codius, NXT, Namecoi, Coloredcoins, Helloblock, Counterparty, Mastercoin, Coron, BlockCypher, Chain.com, Chromaway
Currency Exchange & Remittance
Startups: Coinbase (Wallet), BitPeesa, Billion, Ripple, Stellar, Kraken, Fundrs.org, MeXBT, CryptoSigna
P2P Transfer
Startups: BTC Jam, Codius, BitBond, Bitnplay (Donation), DeBuNe (SME’s B2B transactions)
Data Storage
Startups: Storj.io, Peernova
Trading Platforms
Startups: equityBits, Spritzle, Secure Assets, Coins-e, DXMarkets, MUNA, Kraken, BitShares
Games
Startups: PlayCoin, Play (on DACx platform), Deckbound